A factorial research design can be one of __________ types. – A factorial research design, a powerful tool in the researcher’s arsenal, allows for the investigation of multiple independent variables and their interactions within a single experiment. This multifaceted approach provides valuable insights into complex phenomena, enabling researchers to explore the interplay of various factors and their combined effects on the outcome.
Factorial research designs offer a systematic and efficient way to examine the effects of different factors, making them particularly useful in fields such as psychology, education, and medicine. By manipulating multiple variables simultaneously, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the relationships between variables and identify potential interactions that may not be apparent in simpler designs.
Types of Factorial Research Designs: A Factorial Research Design Can Be One Of __________ Types.

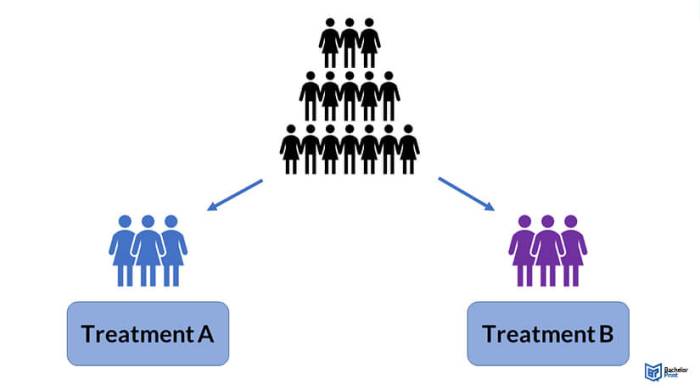
Factorial research designs are a type of experimental design in which two or more independent variables are manipulated simultaneously. This allows researchers to investigate the effects of each independent variable, as well as the interactions between them.
There are several different types of factorial research designs, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of factorial research designs include:
- 2×2 factorial design:This is the simplest type of factorial research design, involving two independent variables with two levels each. For example, a researcher might investigate the effects of gender (male vs. female) and age (young vs. old) on voting behavior.
- 3×3 factorial design:This type of factorial research design involves three independent variables with three levels each. For example, a researcher might investigate the effects of gender (male vs. female vs. other), age (young vs. middle-aged vs.
old), and education level (high school vs. college vs. graduate school) on job satisfaction.
- 2×3 factorial design:This type of factorial research design involves two independent variables, one with two levels and the other with three levels. For example, a researcher might investigate the effects of gender (male vs. female) and income level (low vs. middle vs.
high) on consumer spending.
The choice of which factorial research design to use depends on the number of independent variables and levels of each variable that the researcher wants to investigate. It is important to select a design that will provide the most information about the effects of the independent variables and their interactions.
Factors in Factorial Research Designs
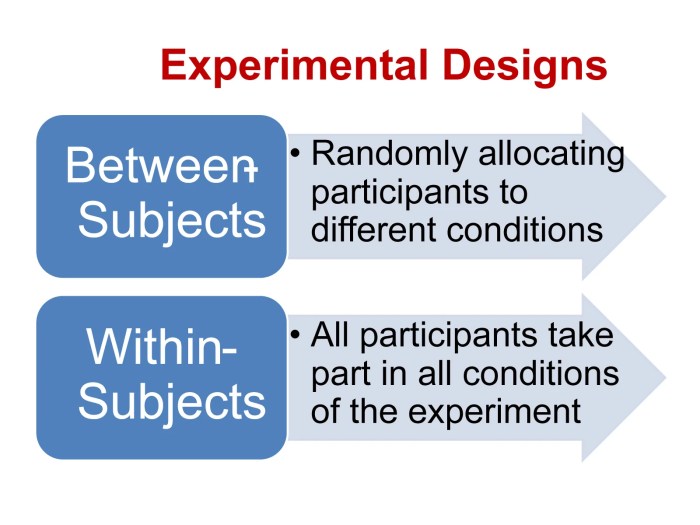
A factor in a factorial research design is an independent variable that is manipulated by the researcher. Factors can be either qualitative or quantitative.
Qualitative factorsare factors that are not measured on a numerical scale. For example, gender is a qualitative factor that can be classified as male or female. Quantitative factorsare factors that are measured on a numerical scale. For example, age is a quantitative factor that can be measured in years.
The number of factors and levels of each factor that are included in a factorial research design will determine the number of treatment conditions in the design. For example, a 2×2 factorial design with two qualitative factors with two levels each will have four treatment conditions.
A 3×3 factorial design with three quantitative factors with three levels each will have 27 treatment conditions.
It is important to select factors that are relevant to the research question and that will provide meaningful information about the effects of the independent variables.
Interactions in Factorial Research Designs
An interaction in a factorial research design occurs when the effect of one independent variable depends on the level of another independent variable. For example, a researcher might find that the effect of gender on voting behavior depends on the age of the voter.
Interactions can be either positive or negative. A positive interactionoccurs when the effect of one independent variable is stronger at one level of another independent variable. A negative interactionoccurs when the effect of one independent variable is weaker at one level of another independent variable.
It is important to detect and interpret interactions in factorial research designs because they can provide important information about the relationships between the independent variables.
Analysis of Factorial Research Designs
The data from a factorial research design can be analyzed using a variety of statistical techniques. The most common statistical technique used to analyze factorial research designs is analysis of variance (ANOVA).
ANOVA is a statistical technique that tests for the significance of the effects of the independent variables and their interactions. ANOVA can be used to test for the significance of main effects, which are the effects of each independent variable, and interaction effects, which are the effects of the interactions between the independent variables.
In order to use ANOVA to analyze a factorial research design, the data must meet certain assumptions. These assumptions include:
- The data must be normally distributed.
- The variances of the groups must be equal.
- The observations must be independent.
If the assumptions of ANOVA are not met, then the results of the analysis may not be valid.
Applications of Factorial Research Designs
Factorial research designs are used in a variety of fields of research, including psychology, education, and marketing. Factorial research designs can be used to investigate a wide range of research questions, such as:
- The effects of different teaching methods on student achievement.
- The effects of different marketing campaigns on sales.
- The effects of different drug treatments on patient outcomes.
Factorial research designs are a powerful tool for investigating the effects of multiple independent variables. However, it is important to carefully consider the number of factors and levels of each factor that are included in the design, as well as the assumptions of the statistical techniques that will be used to analyze the data.
FAQ
What are the different types of factorial research designs?
Factorial research designs can be classified into various types, including 2×2 factorial designs, 3×3 factorial designs, and mixed factorial designs. The choice of design depends on the number of factors and levels being investigated.
What are the advantages of using a factorial research design?
Factorial research designs offer several advantages, such as increased efficiency, control over extraneous variables, and the ability to investigate interactions between variables.
What are the limitations of using a factorial research design?
Factorial research designs can be complex to design and analyze, and they may require a large sample size. Additionally, interactions between variables can be difficult to interpret.