Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Heating Cooling Curve Worksheet Answer Key. This document is designed to provide you with a thorough understanding of the fundamentals, applications, calculations, and data analysis involved in heating and cooling curves. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or professional in the field, this resource will serve as an invaluable tool for expanding your knowledge and enhancing your understanding of this critical aspect of materials science.
Heating and cooling curves are graphical representations of the temperature changes that occur in a substance as it undergoes heating or cooling. They provide valuable insights into the physical and chemical properties of materials, making them essential tools in various scientific and industrial applications.
This guide will delve into the intricacies of heating and cooling curves, empowering you with the knowledge to effectively interpret and utilize this data in your own research and practice.
Heating and Cooling Curve Basics
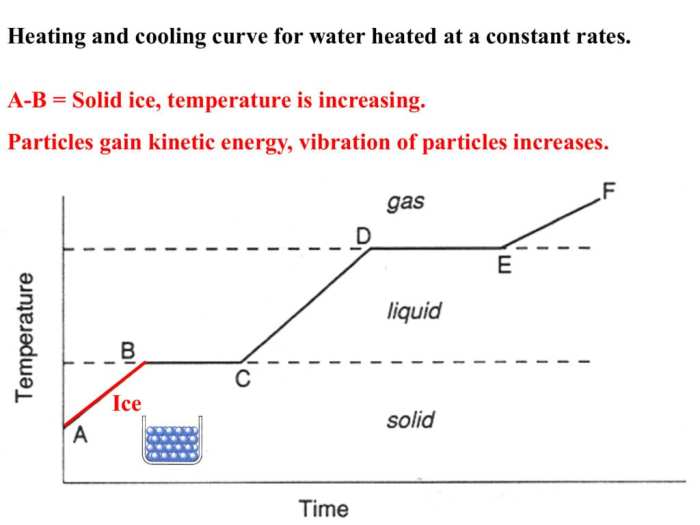
A heating and cooling curve is a graphical representation of the temperature of a substance as it is heated or cooled. The curve can be used to identify the different stages of a substance’s phase transition, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation.
The different stages of a heating and cooling curve are:
- Solid phase:The substance is in a solid state and its temperature is increasing.
- Melting:The substance is melting and its temperature remains constant.
- Liquid phase:The substance is in a liquid state and its temperature is increasing.
- Boiling:The substance is boiling and its temperature remains constant.
- Gas phase:The substance is in a gas state and its temperature is increasing.
The relationship between temperature and time on a heating and cooling curve is linear. The slope of the curve is equal to the rate of heating or cooling.
Heating and Cooling Curve Applications
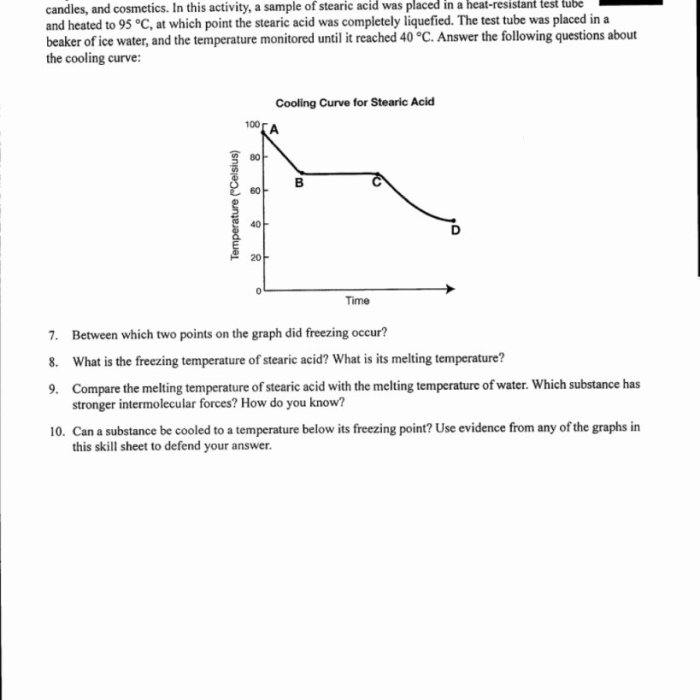
Heating and cooling curves are used in materials science to identify and characterize materials. The curves can be used to determine the melting point, boiling point, and specific heat capacity of a substance. Heating and cooling curves can also be used to study the phase transitions of materials.
In industry, heating and cooling curves are used to control the manufacturing process of materials. The curves can be used to ensure that the material is heated or cooled at the correct rate to achieve the desired properties.
Heating and Cooling Curve Calculations: Heating Cooling Curve Worksheet Answer Key
The enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization can be calculated from a heating and cooling curve. The enthalpy of fusion is the amount of heat required to melt a solid substance. The enthalpy of vaporization is the amount of heat required to vaporize a liquid substance.
The formulas for calculating the enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization are:
- Enthalpy of fusion: ΔH fus= mΔT fus
- Enthalpy of vaporization: ΔH vap= mΔT vap
where:
- ΔH fusis the enthalpy of fusion (J)
- ΔH vapis the enthalpy of vaporization (J)
- m is the mass of the substance (g)
- ΔT fusis the change in temperature during melting (°C)
- ΔT vapis the change in temperature during vaporization (°C)
The errors that can occur when calculating the enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization from a heating and cooling curve include:
- Errors in measuring the mass of the substance
- Errors in measuring the temperature change
- Errors in determining the melting point and boiling point
Heating and Cooling Curve Data Analysis
Heating and cooling curve data can be analyzed to determine the melting point, boiling point, and specific heat capacity of a substance.
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid substance melts. The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid substance boils. The specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1°C.
To determine the melting point and boiling point of a substance from a heating and cooling curve, the following steps are followed:
- Locate the point on the curve where the substance begins to melt or boil.
- Draw a horizontal line from the point where the substance begins to melt or boil to the temperature axis.
- The melting point or boiling point is the temperature at which the horizontal line intersects the temperature axis.
To determine the specific heat capacity of a substance from a heating and cooling curve, the following steps are followed:
- Calculate the slope of the linear portion of the curve.
- The specific heat capacity is equal to the slope of the linear portion of the curve multiplied by the mass of the substance.
The limitations of using heating and cooling curve data to determine the melting point, boiling point, and specific heat capacity of a substance include:
- The accuracy of the results depends on the accuracy of the measurements.
- The results may be affected by the presence of impurities in the substance.
- The results may be affected by the rate of heating or cooling.
Popular Questions
What is a heating cooling curve?
A heating cooling curve is a graphical representation of the temperature changes that occur in a substance as it undergoes heating or cooling.
What are the different stages of a heating cooling curve?
The different stages of a heating cooling curve include the solid phase, melting phase, liquid phase, and vapor phase.
How are heating cooling curves used in materials science?
Heating cooling curves are used in materials science to identify and characterize materials, study phase transitions, and determine thermodynamic properties.